Automotive PPAP (Production Part Approval Process) ensures parts meet strict quality standards before mass production. This guide will cover its key elements, submission levels, and critical processes, providing everything you need to master automotive PPAP.
Key Takeaways
- PPAP is essential in the automotive industry for verifying that suppliers produce parts meeting strict quality standards and specifications.
- The PPAP process consists of 18 key elements, including design and engineering documentation, approvals, several analysis processes, sample production parts, and the Part Submission Warrant which summarizes the entire PPAP submission. Each process is tailored to customer requirements.
- Digitizing PPAP processes is set up to enhance efficiency and accuracy, and utilize tools to improve documentation and communication.
Understanding Automotive PPAP
The Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) is the bedrock of quality assurance in the automotive industry. This standardized method verifies a supplier’s ability to produce parts that consistently meet engineering specifications and quality standards. PPAP serves as a rigorous approval process for new or revised parts, ensuring that every component delivered can be reliably produced in mass quantities.
PPAP is not just a formality; it’s a crucial communication tool that minimizes the risk of errors and misunderstandings between suppliers and manufacturers. Setting clear expectations and using a structured approach, PPAP aligns all parties on quality and performance requirements. This alignment is vital in the automotive and aerospace industries, where even a minor defect can lead to significant issues.
Suppliers are responsible for maintaining a comprehensive documentation system that includes all PPAP elements and creating a detailed PPAP report. This report is then reviewed by the manufacturing quality or engineering team for approval. The process not only enhances the quality management system but also aligns with IATF 16949 requirements, ensuring a robust automotive supply chain.
PPAP and its Relationship with APQP, ISO 9001, and IATF 16949
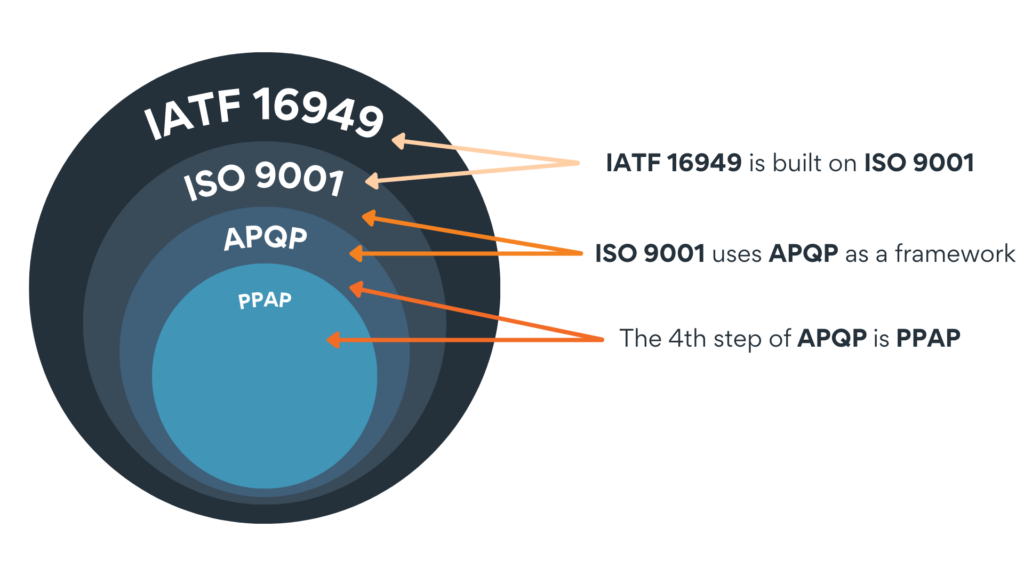
PPAP is a set of processes that are part of several other frameworks or standards. To achieve certification of these standards, PPAP is required.
PPAP is a part of the Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP). APQP is a framework used to introduce new products or modify existing ones, ensuring systematic quality management throughout the product lifecycle. Within this framework, it serves as a critical component that confirms production processes consistently produce parts that meet stringent quality standards. In addition to PPAP, the APQP approach includes planning, process design and development, and product and process validation.
The successful implementation of APQP directly influences PPAP outcomes, enhancing overall quality and efficiency. PPAP functions as a verification tool within the APQP process, ensuring that all production remains consistent and reliable.
APQP is part of ISO 9001, which is the international standard for quality management. ISO 9001 provides a framework to ensure organizations consistently provide products and services that meet their customer needs and various regulatory requirements. ISO 9001 requires organizations to have a QMS in place.
One level above ISO 9001 is IATF 16949, the international standard for automotive quality management systems. IATF 16949 is based on ISO 9001, but it also includes customer-specific requirements for each automaker.
By integrating APQP and PPAP, manufacturers can achieve a seamless and effective quality assurance system and help ensure their certification for ISO 9001 and IATF 16949.
Key Elements of Automotive PPAP

The heart of the PPAP process lies in its 18 key elements, each designed to ensure that the production process can consistently yield quality parts. These elements range from design documentation and engineering change notices to customer engineering approval, all working together to create a reliable and repeatable process. Selecting the appropriate PPAP submission level depends on factors such as part complexity, criticality to function, and the supplier’s experience.
The Part Submission Warrant (PSW) is a critical document within the PPAP package. It includes detailed information like drawing numbers, material declarations, and any deviations from standard requirements. The PSW serves as a summary of the entire PPAP submission, providing a snapshot of all essential approvals and supporting information.
Each step in the PPAP process is tailored to meet specific customer requirements, ensuring that the final product aligns perfectly with expectations.
1. Design Documentation
Design documentation is the cornerstone of PPAP, ensuring that the parts delivered align perfectly with customer requirements. This documentation must include both the supplier’s and customer’s drawings, as well as a purchase order to verify part specifications. A part drawing in the PPAP package confirms possession of the drawing and verifies that the part meets customer specifications.
The design documentation serves as a detailed description of the part, providing all necessary supporting data to confirm correct part delivery. This alignment is essential for maintaining the integrity of the production part approval process and ensuring that every component produced is up to standard.
2. Engineering Change Notice (ECN)
An Engineering Change Notice (ECN) is vital when any modifications to a part are requested. This document must be included in the PPAP package and requires customer approval. The ECN ensures that all changes are documented and communicated clearly, maintaining alignment with customer requirements and expectations.
3. Customer Engineering Approval
Customer engineering approval is a critical step in the PPAP process. It ensures that production parts meet the stringent specifications set by the customer. Evidence of this approval must be included in the PPAP submission, providing assurance that the parts will perform as expected in real-world conditions.
4. Design Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (DFMEA)
Design Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (DFMEA) is a strategy used during the design phase of a product. It helps the design team identify and record possible ways the product could fail before the design is finished. By doing this, they can take steps to prevent these failures from occurring.
Submission Levels in Automotive PPAP
The Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) includes five distinct submission levels, each dictating specific requirements for part approval. These levels are:
- Level 1: Requires only the Part Submission Warrant (PSW).
- Level 2: Involves the PSW along with sample production parts.
- Level 3: Requires the PSW, product samples, and limited supporting data.
- Level 4: Involves the PSW, product samples, and additional supporting data.
- Level 5: Requires the PSW along with product samples and comprehensive supporting data.
The choice of submission level depends on factors such as part complexity and customer requirements.
Level 3 is the default submission level for most automotive parts, reflecting a comprehensive yet standard requirement. It includes the PSW, product samples, and all relevant supporting documentation. This level ensures a thorough review and approval process, balancing the need for detailed information with practical efficiency.
In contrast, Level 4 submissions are tailored to specific customer requirements and may involve additional documents or data. This flexibility allows for a customized approach, ensuring that all necessary information is provided to meet customer expectations. The varying submission levels ensure that the PPAP process is adaptable and can cater to the unique needs of different parts and customers.
Critical Processes in Automotive PPAP
Critical processes within the PPAP framework are designed to ensure that automotive parts meet the highest quality and reliability standards throughout the production process. By identifying potential issues early, the PPAP process reduces the risks of costly mistakes and recalls, ensuring a smooth and efficient production flow.
Automating tasks within the PPAP process can significantly enhance efficiency and reduce manual errors. This automation allows for more accurate and timely data collection, improving overall process reliability and repeatability.
5. Process Flow Diagram
A process flow diagram is essential for detailing the sequence of steps involved in part manufacturing, including the flow of materials. This diagram provides a clear visual representation of the production process, helping to identify potential bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
6. Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (PFMEA)
Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (PFMEA) is a systematic approach used to identify potential failures, including design failure mode, and document controls during the manufacturing process. By analyzing each stage of production, PFMEA helps to preemptively identify and mitigate risks, ensuring a stable and reliable manufacturing environment.
Initial process studies use Statistical Process Control (SPC) to analyze and ensure that critical characteristics are consistently met. These studies confirm that production processes are stable and functioning within desired limits, providing a solid foundation for quality assurance.
7. PFMEA Control Plan
The PFMEA control plan includes detailed descriptions of characteristics and inspection methods to ensure production stability. It must correspond with the process flow diagram and PFMEA, detailing all manufacturing steps, including the handling of non-conforming materials.
Measurement and Validation in Automotive PPAP

Measurement and validation are vital components of the PPAP process, ensuring that parts meet specified quality standards and customer requirements. This involves a thorough validation check to ensure that measurement specifications on drawings align with actual results. Proper documentation ensures all testing results and compliance records are readily accessible for review.
A robust measurement system analysis (MSA) confirms that the tools used for measuring parts are accurate and reliable. This step is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the quality assurance process and ensuring that all parts meet the necessary standards.
8. Measurement System Analysis (MSA)
Measurement Systems Analysis (MSA) studies help confirm that measurement tools are accurately calibrated for consistent results. Calibration records are essential in MSA as they document the precision of measurement instruments. This ensures that the measurement process is reliable, thereby enhancing the overall quality assurance efforts within the automotive PPAP framework.
MSA is a cornerstone of quality management systems, providing a comprehensive risk assessment that supports the entire PPAP process. Accurate and reliable measurement systems ensure that parts consistently meet customer expectations.
Initial Process Studies
Initial process studies focus on using SPC charts for critical characteristics to ensure processes are stable. These studies include statistical process control (SPC) methods to monitor and control production processes, demonstrating the reliability of critical processes within the manufacturing environment.
These studies are essential for confirming that the production processes are stable and functioning within desired limits. By validating the reliability of these processes, manufacturers can ensure a consistent and high-quality output.
9. Dimensional Results
Dimensional results are recorded using a spreadsheet, which includes every dimension on the part drawing, measurement results, product characteristics, specifications, and an assessment of pass/fail.
This detailed documentation is crucial for validating measurement accuracy for PPAP submission.
10. Records of Material and Performance Tests
Records of material and performance tests ensure that all materials used in the production process meet the required specifications and performance standards. The documentation includes detailed results from tests conducted on materials and parts, verifying their compliance with customer requirements and industry standards.
Performance tests evaluate the functionality and durability of parts under various conditions, ensuring they can withstand real-world applications. These tests confirm that the parts not only meet design specifications but also perform reliably throughout their intended lifespan.
11. Initial Process Studies
The initial process studies demonstrate that the most critical processes are stable and ready to begin validation. They usually include SPC charts (Statistical Process Control), which are graphs that track data over time to assess performance and progress.
Documentation and Reporting in Automotive PPAP
Documentation and reporting are fundamental to the PPAP process, ensuring that all necessary records are maintained and accessible for review. This includes design records, authorized engineering changes, engineering approval, dimensional results, control plans, and customer-specific requirements. Comprehensive documentation is essential for meeting PPAP requirements and securing approval.
Common challenges in the PPAP process include incomplete documentation and lack of standardization across submissions. Addressing these challenges is crucial for maintaining a robust quality management system and ensuring a smooth approval process.
12. Qualified Laboratory Documentation
Certifications from qualified laboratories are essential for validating tests conducted during the PPAP process. These laboratories must meet industry certifications to ensure the integrity and reliability of validation testing.
Qualified laboratory documentation includes certifications from labs for all testing performed, both in-house and externally.
13. Appearance Approval Report (AAR)
The Appearance Approval Report (AAR) is essential for confirming that the product’s appearance aligns with the specified customer requirements. This report ensures that the final product has been inspected and adheres to all specified aesthetic requirements.
14. Sample Production Parts
While it is not possible to include sample product parts themselves in a report, a picture of the part and notes on where it is stored is included for review and possible physical retrieval.
15. Master Sample
The master sample is a sample part that has been signed off on by both the customer and the supplier. Often this part is used to train operators on subjective inspections, such as for visual or noise properties.
16. Checking Aids
Imagine a detailed list of all the tools used to inspect, test, and measure a part during the assembly process and you’ll be looking at a checking aid. The checking aid list includes the tool name, description, and its calibration schedule that was used for creating the part.
17. Records of Compliance with Customer Specific Requirements
The Records of Compliance with Customer Specific Requirements is considered a critical element in the PPAP submission package becasue it ensures that the supplier fully understands and complies with all customer requirements. The documentation must demonstrate a supplier’s adherence to any unique requirements outlined by the customer, including specific industry standards, quality parameters, or special handling instructions. Essentially, it proves that the produced parts meet all the customer’s particular needs beyond standard specifications.
18. Part Submission Warrant (PSW)
The Part Submission Warrant (PSW) summarizes the entire PPAP submission process. It includes a detailed report of dimensional results and serves as a benchmark for future production. This document is crucial for obtaining PPAP submission approval.
Digitizing the Automotive PPAP Process

Digital tools and platforms can significantly streamline the traditionally manual steps involved in PPAP. Digital tools enable real-time tracking of the PPAP process, improving transparency and accountability. Advanced digital solutions facilitate quicker identification and resolution of issues, which leads to improved product quality.
One example is the model-based definition (MBD) approach. MBD uses 3D CAD models as the primary source of information for generating PPAP reports. This approach reduces time and errors, improves inspection generation, and enhances uniformity across suppliers. Compared to 2D drawings, MBD provides a more accurate and efficient way to handle part specifications and documentation.
Digitizing the PPAP process not only enhances efficiency but also ensures a more reliable and repeatable process. By embracing digital solutions, manufacturers can stay ahead in the competitive automotive industry and meet the highest quality standards.
Summary
In summary, the Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) is an indispensable tool in the automotive industry, ensuring that every part meets high-quality standards and customer specifications. From understanding the key elements and submission levels to delving into critical processes and measurement validation, we have explored the comprehensive framework that PPAP provides. The digitization of PPAP and its integration with APQP further enhance the efficiency and reliability of the entire process.
By mastering PPAP, manufacturers can significantly reduce the risks of errors, improve communication, and ensure consistent production quality. Embracing these practices not only strengthens the supply chain but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement and excellence. As you navigate the complexities of automotive manufacturing, let PPAP be your guide to achieving unparalleled quality assurance.
If your company deals with PPAP and its guiding standards, it’s important to have the right partners to ensure success. EMDS expertise in this area can make all the difference. We offer quality compliance consulting, expert QMS development and maintenance, and numerous training options for your team. Connect with us for more information!

